Gula, also known as Ninkarrak, Ninisinna, or Bau, is a significant deity in ancient Mesopotamian mythology, revered primarily as the goddess of healing and medicine. Her worship was widespread throughout Mesopotamia, particularly in cities such as Isin, Nippur, and Babylon. Gula’s role as a healer places her in a compassionate and protective position within the pantheon, where she is often invoked for her abilities to cure diseases and protect against ailments.
Gula is depicted as a healer who possesses profound medical knowledge and the ability to restore health. She is often shown accompanied by her sacred dogs, which are symbols of her healing powers. These dogs are sometimes considered to be her emissaries, sent out to help heal the sick. Gula is also associated with the ability to resurrect the dead, showcasing her as a powerful figure capable of overcoming the boundaries between life and death.
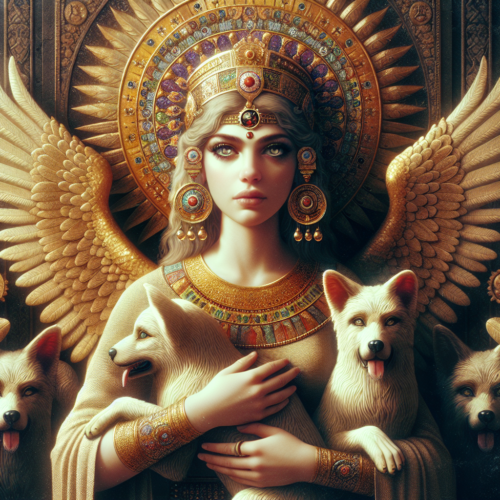

In iconography, Gula is frequently depicted with a canine companion, emphasizing her connection to healing and protection. She may also be shown holding medicinal plants or potions, further symbolizing her role as a goddess of healing. Her symbols often include the star and the stylus, linking her to aspects of divination and writing, which were important in the diagnostic processes of Mesopotamian medicine.
While specific myths focusing solely on Gula are rare, she appears in various texts and prayers where her healing powers are invoked. She is often called upon in incantations and rituals designed to ward off diseases or to heal the sick, reflecting her integral role in the everyday lives of the Mesopotamian people.
Gula’s legacy as a goddess of healing extends into the broader context of ancient medicine and public health. Her veneration highlights the ancient Mesopotamians’ approach to health and disease, which combined both spiritual and practical elements. Today, Gula is often referenced in studies of ancient medicine and religion, serving as a testament to the sophisticated understanding of health and healing in ancient Mesopotamian culture.